This transaction also generates a profit of $1,000 for Sam Enterprises, which would increase the owner’s equity element of the equation. At this time, there is external equity or liability in Sam Enterprise. The only equity is Sam’s capital (i.e., owner’s job cost management vs xero equity amounting to $100,000). The rights or claims to the properties are referred to as equities. So, let’s take a look at every element of the accounting equation. In other words, all assets initially come from liabilities and owners’ contributions.
What Are the Key Components in the Accounting Equation?
- However, due to the fact that accounting is kept on a historical basis, the equity is typically not the net worth of the organization.
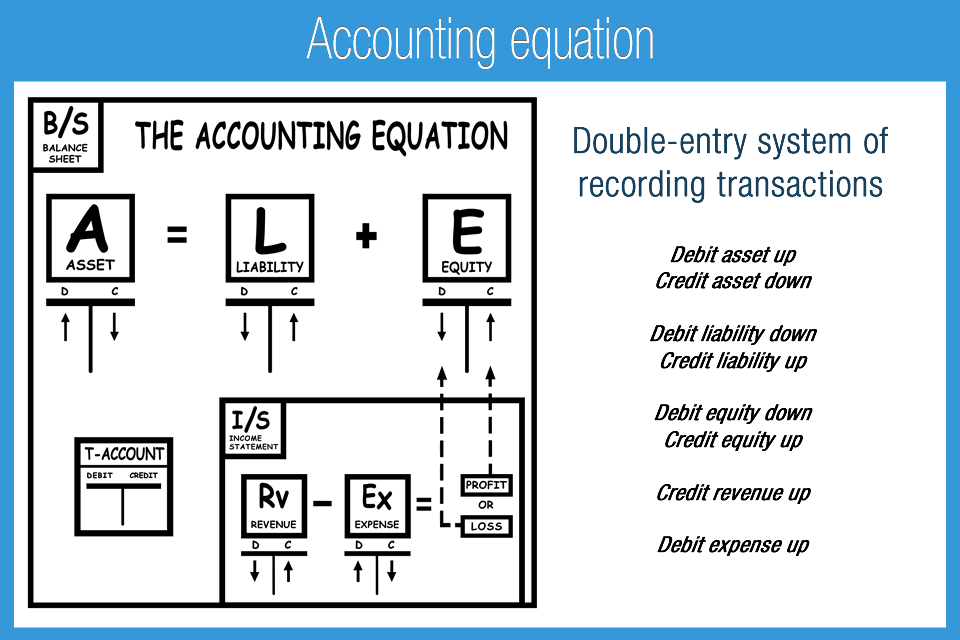
- As its name implies, the Accounting Equation is the equation that explains the relationship of accounting transactions.
- Ted is an entrepreneur who wants to start a company selling speakers for car stereo systems.
- This lesson presented the basic accounting equation and how it stays equal.
- Now that we have a basic understanding of the equation, let’s take a look at each accounting equation component starting with the assets.
We also show how the same transaction affects specific accounts by providing the journal entry that is used to record the transaction in the company’s general ledger. Shareholders’ equity is the total value of the company expressed in dollars. Put another way, it is the amount that would remain if the company liquidated all of its assets and paid off all of its debts. The remainder is the shareholders’ equity, which would be returned to them. Essentially, the representation equates all uses of capital (assets) to all sources of capital, where debt capital leads to liabilities and equity capital leads to shareholders’ equity. Equity includes any money that has been invested into the company by shareholders as well as retained earnings which have not yet been paid to shareholders as dividends.
Arrangement #3: Assets = Liabilities + Owner’s Capital – Owner’s Drawings + Revenues – Expenses
This is how the accounting equation of Laura’s business looks like after incorporating the effects of all transactions at the end of month 1. The accounting equation is fundamental to the double-entry bookkeeping practice. Its applications in accountancy and economics are thus diverse.
Company
The shareholders’ equity number is a company’s total assets minus its total liabilities. Shareholder Equity is equal to a business’s total assets minus its total liabilities. It can be found on a balance sheet and is one of the most important metrics for analysts to assess the financial health of a company. As you can see, all of these transactions always balance out the accounting equation.
Liabilities
The accounting equation ensures that the balance sheet remains balanced. That is, each entry made on the debit side has a corresponding entry (or coverage) on the credit side. With the accounting equation expanded, financial analysts and accountants can better understand how a company structures its equity.
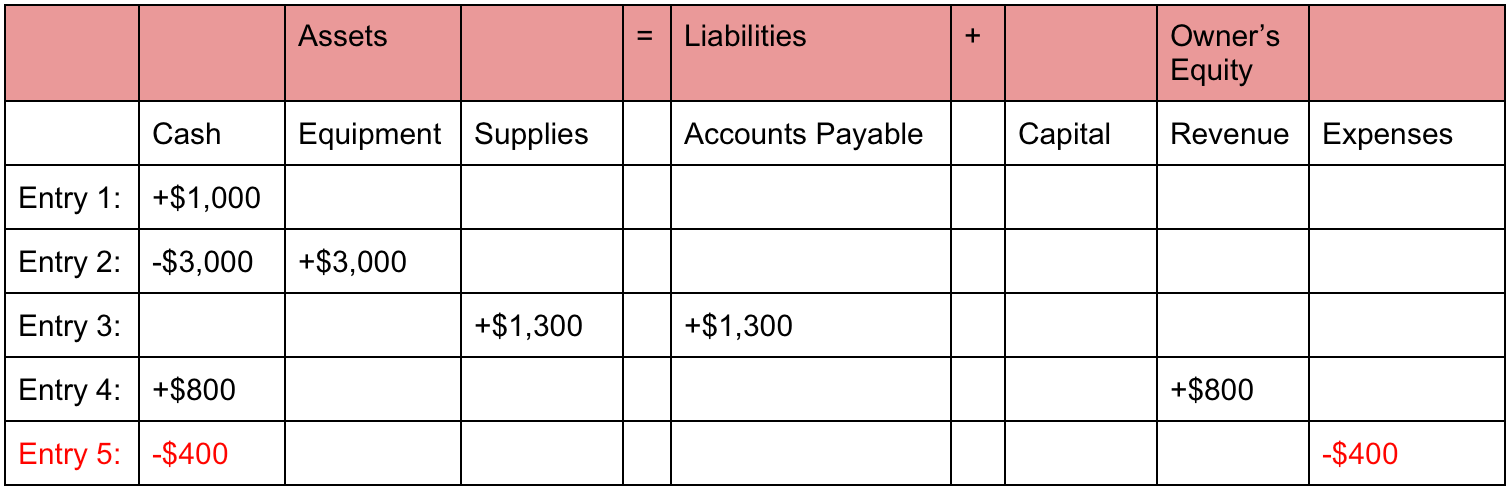
Single-entry accounting only shows expenses and sales but doesn’t establish how those transactions work together to determine profitability. On 10 January, Sam Enterprises sells merchandise for $10,000 cash and earns a profit of $1,000. As a result of this transaction, an asset (i.e., cash) increases by $10,000 while another asset ( i.e., merchandise) decreases by $9,000 (the original cost).
The asset of cash decreases by £400 but a new asset (the iPad) enters the equation at a £400 valuation. Non-current assets are often written as “NCA”; current assets as “CA”; current liabilities as “CL… you get the idea. Previously, a non current asset used to be called a fixed asset. Largely because those assets tend to be “fixed” (e.g., buildings). Assets held for the long term are called “Non-current assets”. That’s because they’re assets that will be used in not just the current period (hence “non-current”).
Net value refers to the umbrella term that a company can keep after paying off all liabilities, also known as its book value. It specifically highlights the amount of ownership that the business owner(s) has. A financial professional will offer guidance based on the information provided and offer a no-obligation call to better understand your situation.
